Ovarian Cancer
Navigate To:
What is Ovarian Cancer?
The ovaries are small, olive-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries are a part of the female body that produces eggs. Ovarian cancer is the cancerous growth that begins in the ovary. The ovarian cancer can start in the ovary’s germ, stromal, or epithelial cells. Germ cells become eggs, stromal cells make up the substance of the ovary and epithelial cells are the outer layer of the ovary.
What are the Types of Ovarian Cancer?
The type of cell where the cancer begins will determine the type of ovarian cancer you have, they include the following:
- Epithelial tumors, begin in the thin layer of tissue covering the outside of the ovaries.
- Germ cell tumors, begin in the egg-producing cells and these rare ovarian cancers occur in younger women.
- Stromal tumors, begin in the ovarian tissue that contains hormone-producing cells. These tumors are diagnosed at an earlier stage unlike other ovarian tumors.
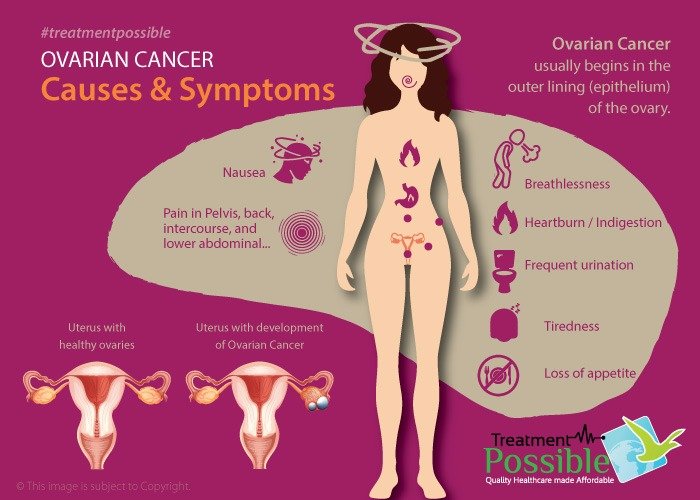
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
In the early stages, there are few or no symptoms. If symptoms do occur, they may resemble those of other conditions, such as premenstrual syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, or a temporary bladder problem. However the symptoms will worsen and the ovarian cancer may include:
- Abdominal swelling or bloating
- feeling full rapidly when eating
- Gas or indigestion
- Unintentional weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- pain in the pelvis or abdomen
- pain in the back or abdomen
- changes in urination patterns, such as more frequent urination.
- changes in bowel movements, such as constipation and Diarrhoea.
- fatigue
- Breathlessness and severe abnormal vaginal bleeding are life-threatening symptoms.
The symptoms change if the cancer spreads to other parts of the body.
Are you facing similar symptoms?
Consult an Experienced Doctor online for a free diagnosis
What are the Risk factors for Ovarian Cancer?
A number of factors increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer. Not all women having risk factors will get ovarian cancer. Risk factors for ovarian cancer include:
- Age over 55 years
- Having a family history of ovarian cancer, breast cancer or colon cancer
- First pregnancy after the age of 35
- People who never had children are at higher risk.
- Obesity
- Smoking
- If you Have taken hormone therapy after menopause
- Early menstruation and Late menopause – When menstruation starts at an early age (before 12 years of age) or getting menopause later, increases the risk of ovarian cancer.
- The “breast cancer genes” BRCA1 and BRCA2 are also linked to ovarian cancer risk.
How is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed?
Tests and procedures needed to diagnose ovarian cancer include:
- Pelvic exam: During a pelvic exam, your physician will insert gloved fingers into your vagina and and at the same time presses a hand on your abdomen in order to feel (palpate) your pelvic organs. The physician will also visually examine your external genitalia, vagina and cervix.
- Imaging tests: An ultrasound or CT scans of your abdomen and pelvis, can help to determine the size, shape and structure of your ovaries. Other imaging tests will include a CT scan, MRI, and PET scan.
- Blood tests: Blood tests include organ function tests that help to determine your overall health. Your doctor may also test your blood for tumor markers which indicate ovarian cancer. Such as, a test for cancer antigen 125 levels, which may be elevated if you have ovarian cancer, a test for HCG levels, which may be elevated if you have a germ cell tumor, a test for inhibin, estrogen, and testosterone levels, which may be elevated if you have a stromal cell tumor.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is essential to determine if cancer is present. During the procedure, a small tissue sample is taken from the ovaries to check for cancer cells. This is done with a needle guided by a CT scan or by an ultrasound. It can also be done through a laparoscope. If fluid is present in the abdomen, a sample can be examined for cancer cells.
When your doctor is not certain of your diagnosis, the signs of cancer are tested after removing the ovaries by surgery.
If a healthcare professional diagnoses ovarian cancer, they will have to determine the stage and grade to decide on a treatment plan. The grade refers to how abnormal the cancer cells appear.
Want more clarification about medical expense & treatment plan?
Plan your treatment in India
What are the Stages of Ovarian Cancer?
The stages of ovarian cancer can be determined by three factors:
- the size of the tumor
- If the tumor has invaded tissues in the ovary or nearby tissues.
- If the cancer has spread to other areas of the body.
There are 4 stages of the ovarian cancer:
- Stage 1 cancer is within one or both ovaries. (Cancer cells have not spread elsewhere.)
- Stage 2 cancer is within the pelvis. (Cancer cells have not spread elsewhere.)
- Stage 3 cancer has spread into the abdomen or to the nearby organs, such as the uterus.
- Stage 4 cancer has spread outside the abdomen or to other organs such as the lungs or liver.
In each stage there are sub-stages, these sub-stages tell your doctor a bit more about your cancer. For example, stage 1A ovarian cancer is cancer that has developed in only one ovary and stage 1B cancer has developed in both the ovaries.
